数据结构-块状链表
概述
块状链表 是一种比较中庸的数据结构。它将 “分块思想” 应用于链表之中,从而整合了线性表与链表的优缺点,使得其上操作的时间复杂度均为 $O(\sqrt{N})$。
其结构图大致如下:
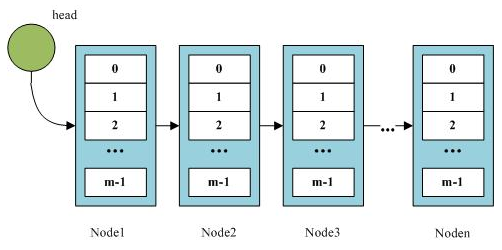
假定数据总量为 $N$,将这些数据均分为 $\sqrt{N}$ 块,块内数据使用线性表进行存储,块间使用引用进行链接,如此组织便是块状链表。对块状链表操作时,首先需要花费 $O(\sqrt{N})$ 时间定位到块,随后花费 $O(\sqrt{N})$ 在块内执行操作,故而操作的时间复杂度为 $O(\sqrt{N})$。
“分块思想” 其本质为一棵仅有三层的多叉树,其结构如图所示。
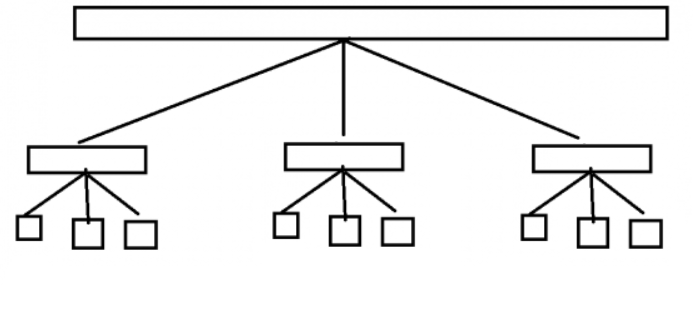
结构
块状链表中存储的数据量大小通常是未知的,故而通常需要预估数据量大小以指定块大小。
1 | class BlockList<E> { |
实现
块状链表中块大小及块个数决定着操作的时间复杂度,因此每次操作后需要对此二者进行一定调整。
辅助方法
相邻块合并
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10private void unionBlock(Node<E> e1, Node<E> e2) {
// 合并线性表中元素
for (int i = 0; i < e2.blockSize; i++) {
e1.blockArr[e1.blockSize + i] = e2.blockArr[i];
}
// 更新相关字段
e1.blockSize += e2.blockSize;
e1.next = e2.next;
}维护链形态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11private void maintain() {
Node node = this.head;
while (null != node && null != node.next) {
// 如果相邻块中元素个数小于指定的块大小,则需要进行合并。
if (node.blockSize + node.next.blockSize < BlockList.BLOCK_SIZE) {
unionBlock(node, node.next);
continue;
}
node = node.next;
}
}在指定位置处分割块
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20private void splitBlock(Node<E> e1, int index) {
// index非法,直接返回即可。
if (index < 0 || index > e1.blockSize) {
return ;
}
// 创建新块,并调整引用。
Node<E> e2 = new Node<>();
e2.next = e1.next;
e1.next = e2;
// 分割线性表中元素。
for (int i = index; i < e1.blockSize; i++) {
e2.blockArr[i - index] = e1.blockArr[i];
e2.blockSize++;
e1.blockArr[i] = null;
}
e1.blockSize = index;
}初始化
1 | public BlockList() { |
查询
查询指定位置的元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13public E get(int index) {
Node<E> node = this.head;
while (null != node) {
if (index >= node.blockSize) {
index = index - node.blockSize;
node = node.next;
} else {
break;
}
}
return null == node ? null : (E) node.blockArr[index];
}操纵
块状链表中添加元素
我们假定块中元素个数始终小于指定的块大小。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31public void insert(int index, E item) {
// 寻找待插入块及待插入位置
Node<E> node = this.head;
while (true) {
if (index > node.blockSize) {
if (null != node.next) {
index = index - node.blockSize;
node = node.next;
} else {
// 插入位置有误,直接返回即可。
return ;
}
} else {
break;
}
}
// 插入元素至指定位置。
for (int i = node.blockSize; i > index; i--) {
node.blockArr[i] = node.blockArr[i - 1];
}
node.blockArr[index] = item;
node.blockSize++;
// 插入元素后,如果块已满,则需要从中部分割块。
if (node.blockSize == BlockList.BLOCK_SIZE) {
splitBlock(node, BlockList.BLOCK_SIZE / 2);
}
maintain();
}块状链表中删除元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26public void delete(int index) {
// 寻找待删除块及待删除位置
Node<E> node = this.head;
while (null != node) {
if (index >= node.blockSize) {
index = index - node.blockSize;
node = node.next;
} else {
break;
}
}
// 没有找到,直接返回即可。
if (null == node) {
return;
}
// 删除指定元素。
for (int i = index; i < node.blockSize - 1; i++) {
node.blockArr[i] = node.blockArr[i + 1];
}
node.blockSize--;
node.blockArr[node.blockSize] = null;
maintain();
}
相关文章