数据结构-斐波那契堆
概述
斐波那契堆 属于一种构建极为精妙的堆。它由二项队列改造而成,并将懒惰合并及左式堆的 decreaseKey() 实现方法融入其中,最终造就除删除操作外的所有操作的平均时间复杂度为 $O(1)$。
其结构图大致如下:
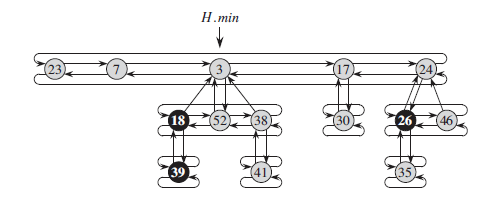
斐波那契堆是具有堆序结构的有根树的集合,该集合中允许具有相同高度的有根树同时存在。该有根树是一棵具有一定限制的树,而正是该种限制,使得有根树中节点数量 $N$ 与根结点的孩子节点数量 $R$ 间具有如下关系: $R = O(log^N)$ ,该关系保证了斐波那契堆之上所有操作的平均时间复杂度。
- 懒惰合并及左式堆的
decreaseKey()实现方法见之前文章。- 斐波那契堆理论上具有良好的性能,但是由于其编程复杂性及时间复杂度的常数因子过大,使得其并不常用。
结构
斐波那契堆中节点结构极其复杂,涉及四个节点引用,这也使得其编程较为复杂。
1 | class FibonacciHeap<E> { |
实现
辅助方法
合并两个环形链表
1
2
3
4
5
6private void unionLinked(Node<E> e1, Node<E> e2) {
e1.right.left = e2.left;
e2.left.right = e1.right;
e1.right = e2;
e2.left = e1;
}从环形链表中剔除指定节点 (当前节点非环形链表中最后一个节点)
1
2
3
4
5
6private void deleteLinkedNode(Node<E> node) {
node.left.right = node.right;
node.right.left = node.left;
node.left = null;
node.right = null;
}向指定环形链表中添加指定节点
1
2
3
4
5
6private void addLinkedNode(Node<E> node, Node<E> root) {
node.left = root.left;
node.right = root;
root.left = node;
node.left.right = node;
}链接两棵有根树,将根值小者作为根值大者的孩子,并返回最终结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21private Node<E> linkTree(Node<E> e1, Node<E> e2) {
// 保证e1为根值小者,e2为根值大者。
if (comparator.compare(e1.item, e2.item) > 0)
return linkTree(e2, e1);
// 如果e1孩子节点为空,则需调整以指向e2。
if (null == e1.child) {
e2.left = e2;
e2.right = e2;
e1.child = e2;
} else {
addLinkedNode(e2, e1.child);
}
// 更新其他信息
// 按照上述mark定义,此处应当置为false。
e2.parent = e1;
e2.mark = false;
e1.degree++;
return e1;
}根链表有根树合并
根链表指代
min字段指向的那个环形链表。该部分做法与懒惰二项队列合并相同高度的二项树做法类似。具体步骤如下:
- 构建一个集合,用于存放含有不同度数的有根树。
- 每次从环形链表中取出一棵有根树,如果集合中存在相同度数的有根树则合并,否则直接将其置于集合中即可。
- 根据集合,构建出一个环形链表,将
min字段指向最小节点即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42private void union() {
// 估计有根树的最大度数。
int rootNum = (int)Math.floor(Math.log(this.currentSize) / Math.log(2));
// 初始化一个存放相同度数有根树集合。
Node<E>[] trees = new Node[rootNum];
// 每次从根链表中提取一个节点,将其置于有根树集合中。
while (true) {
Node<E> node1 = this.min.right;
if (node1 == this.min) {
break;
}
deleteLinkedNode(node1);
int degree = node1.degree;
// 如果链表集当前度数位置不为空,表明需进行合并。
while (null != trees[degree]) {
Node<E> node2 = trees[degree];
node1 = linkTree(node1, node2);
trees[degree] = null;
degree++;
}
trees[degree] = node1;
}
// 将有根树集合中的树恢复为根链表,并更新min字段。
for (int i = 0; i < trees.length; i++) {
if (null == trees[i]) {
continue;
}
if (null == this.min) {
this.min = trees[i];
this.min.left = this.min;
this.min.right = this.min;
} else {
addLinkedNode(trees[i], this.min);
this.min = comparator.compare(this.min.item, trees[i].item) > 0 ? trees[i] : this.min;
}
}
}相关定理证明得到:斐波那契堆中有根树的最大度数 $D$ 与堆中节点数量 $N$ 之间具有如下关系:$D \leq \lfloor log_{\phi}^N \rfloor, \phi = (1 + \sqrt{5}) / 2 \approx 1.618$。
切除当前节点与父节点间关系,并将当前节点置于根链表之中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15private void cut(Node<E> node, Node<E> parent) {
// 当前节点为父节点唯一节点,则需置空父节点的孩子节点指向,否则将该节点从父节点的孩子节点所在环形链表中删除即可。
if (node.right == node) {
parent.child = null;
} else {
deleteLinkedNode(node);
}
parent.degree--;
// 将当前节点置于根链表之中。
// 按照上述mark定义,此处应当置为false。
addLinkedNode(node, this.min);
node.parent = null;
node.mark = false;
}级联切除
通过
mark字段判断是否需要及时将当前节点置于根链表之中,以保证有根树中节点数量 $N$ 与根结点的孩子节点数量 $R$ 之间的关系。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13private void cascadingCut(Node<E> node) {
Node<E> parent = node.parent;
if (null != parent) {
// 如果当前节点为非根节点,且为第二次失去儿子节点,则应当将其与父节点断开,置于根链表之中。
if (node.mark) {
cut(node, parent);
cascadingCut(parent);
} else {
// 那么这便是首次失去儿子节点,应当将mark置为true。
node.mark = true;
}
}
}初始化
1 | public FibonacciHeap(Comparator<? super E> comparator) { |
查询
查询最小元素
1
2
3public E getMin() {
return null == this.min ? null : this.min.item;
}操纵
斐波那契堆中添加元素
直接将节点置于根链表之中即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18public void insert(E item) {
Node<E> node = new Node<>(item);
if (null == this.min) {
// 将当前节点构成一个双向链表
node.left = node;
node.right = node;
// 设置最小节点指向
this.min = node;
} else {
// 将当前节点插入到根链表之中
addLinkedNode(node, this.min);
// 如果当前节点比最小节点小,则需更新
this.min = comparator.compare(this.min.item, node.item) < 0 ? this.min : node;
}
this.currentSize++;
}斐波那契堆合并
直接将两者根链表合并即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19public void merge(FibonacciHeap<E> fibonacciHeap) {
// 待合并堆为空,或者待合并堆就是当前堆,直接返回即可
if (null == fibonacciHeap.min || fibonacciHeap == this) {
return ;
}
// 如果当前堆为空,则直接将待合并堆赋值给当前堆即可
if (null == this.min) {
this.min = fibonacciHeap.min;
this.currentSize = fibonacciHeap.currentSize;
return ;
}
// 二者皆不为空,先合并根链表,然后更新最小节点
this.min = unionLinked(this.min, fibonacciHeap.min);
this.min = comparator.compare(this.min.item, fibonacciHeap.min.item) > 0 ? fibonacciHeap.min : this.min;
this.currentSize = this.currentSize + fibonacciHeap.currentSize;
}斐波那契堆中指定节点降低元素值
具体实现与左式堆中
decreaseKey()操作实现类似。如果指定节点降低元素值后当前有根树不满足堆序性质,则将当前节点所在子树置于根链表之中,同时调整当前有根树。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22public void decreaseKey(Node<E> node, E item) {
// 如果待赋值大于当前节点值,直接返回即可。
if (comparator.compare(node.item, item) < 0) {
return ;
}
node.item = item;
Node<E> parent = node.parent;
// 当前节点父节点不为空,表明非有根树的根结点。另外如果减值后值小于父节点值,则需要进行调整以保证堆序
if (null != parent && comparator.compare(node.item, parent.item) < 0) {
// 将当前节点从父节点中清除,并置于根链表之中。
cut(node, parent);
// 级联切除
cascadingCut(parent);
}
// 减值后的值小于最小节点值,则应当更新最小节点。
if (comparator.compare(node.item, this.min.item) < 0) {
this.min = node;
}
}斐波那契堆中删除最小节点
删除最小节点后,可能根链表中有根树过多,此时需要进行一次集中合并。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37public E deleteMin() {
// 当前堆为空,直接返回空即可。
if (null == this.min) {
return null;
}
Node<E> deleteNode = this.min;
// 待删除节点存在孩子节点,则将其置于当前堆的根链表之中
if (null != deleteNode.child) {
Node<E> tmp = deleteNode.child;
while (null != tmp) {
tmp.parent = null;
tmp = tmp.right == deleteNode.child ? null : tmp.right;
}
this.min = unionLinked(this.min, deleteNode.child);
deleteNode.child = null;
}
// 从当前堆中移除该节点
if (deleteNode.right == deleteNode) {
// 堆中仅有这一个节点,移除后置空最小节点
this.min = null;
} else {
// 这里更新最小节点,并指向待删除节点的右兄弟。此时最小节点指向不需要一定正确,后续会进行union操作。
this.min = deleteNode.right;
// 从根链表中删除最小节点
deleteLinkedNode(deleteNode);
// 删除最小节点使得根链表中节点过多,因此需要整理,顺便找到最小节点。
union();
}
this.currentSize--;
return deleteNode.item;
}斐波那契堆中删除指定节点
具体操作可通过上面两个操作加以实现。
1
2
3
4
5public void delete(Node<E> node) {
decreaseKey(node, this.min.item);
this.min = node;
deleteMin();
}