数据结构-二叉查找树
概述
二叉查找树 是一种特殊的二叉树。对于二叉查找树中每个节点 $X$ 而言,它的左子树中各个节点的值均小于 $X$ 的值,它的右子树中各个节点的值均大于 $X$ 的值。中序遍历二叉查找树,将得到一个递增排序的序列。
其结构图大致如下:
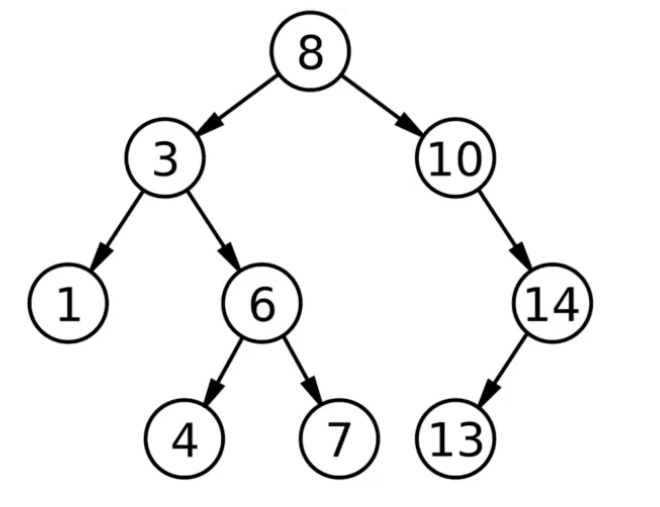
对于一棵含有 $N$ 个节点的二叉树而言,其平均深度为 $log^N$。二叉查找树的各种操作均基于深度实现,故而各种操作的平均时间复杂度为 $O(log^N)$。
结构
为方便实现,规定树中元素各不相同。
1 | class BinarySearchTree<E> { |
实现
辅助方法
树中各种操作往往都需要通过递归实现,二叉查找树的各种操作更是如此。
获取节点的元素计数器
1
2
3private int size(Node<E> node) {
return null == node ? 0 : node.size;
}调整节点的元素计数器
1
2
3
4
5
6private void reSize(Node<E> root) {
if (null == root) {
return ;
}
root.size = size(root.left) + size(root.right) + 1;
}当前子树中查找指定元素是否存在
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17private Boolean containsTree(Node<E> root, E item) {
// 如果当前子树为空,直接返回false即可。
if (null == root) {
return false;
}
if (comparator.compare(root.item, item) > 0) {
// 当前子树根节点值大于待查元素,表明待查元素应该位于左子树之中。
return containsTree(root.left, item);
} else if (comparator.compare(root.item, item) == 0) {
// 等于则直接返回true。
return true;
} else {
// 小于表明待查元素应该位于右子树之中。
return containsTree(root.right, item);
}
}当前子树中插入元素,并返回插入元素后的该子树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16private Node<E> addTree(Node<E> root, E item) {
if (null == root) {
// 向空树中插入元素,直接返回该节点即可。
return new Node<>(item, null, null, 1);
}
if (comparator.compare(root.item, item) > 0) {
// 当前子树根节点值大于待插入元素,表明应当插于左子树之中。
root.left = addTree(root.left, item);
} else if (comparator.compare(root.item, item) < 0) {
// 当前子树根节点值小于待插入元素,表明应当插于右子树之中。
root.right = addTree(root.right, item);
}
reSize(root);
return root;
}当前子树中查找最小元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14private E getMinTree(Node<E> root) {
// 当前子树为空,直接返回空节点即可。
if (null == root) {
return null;
}
if (null == root.left) {
// 当前子树根节点的左儿子为空,表明这是最左节点,此一定为最小元素,故直接返回之。
return root.item;
} else {
// 当前子树根节点的左儿子不为空,则在左子树中查找最小元素。
return getMinTree(root.left);
}
}当前子树中查找最大元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14private E getMaxTree(Node<E> root) {
// 当前子树为空,直接返回空节点即可。
if (null == root) {
return null;
}
if (null == root.right) {
// 当前子树根节点的右儿子为空,表明这是最右节点,此一定为最大元素,故直接返回之。
return root.item;
} else {
// 当前子树根节点的右儿子不为空,则在右子树中查找最大元素。
return getMaxTree(root.right);
}
}当前子树中向下取整
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18private E getFloorTree(Node<E> root, E item) {
// 当前子树为空,直接返回空节点即可。
if (null == root) {
return null;
}
if (comparator.compare(root.item, item) > 0) {
// 当前子树根节点值大于给定元素,则表明floor(item)一定位于左子树之中。
return getFloorTree(root.left, item);
} else if (comparator.compare(root.item, item) == 0) {
// 当前子树根节点值等于给定元素,直接返回即可。
return root.item;
} else {
// 当前子树根节点值小于给定元素,floor(item)可能就是当前元素,或者位于右子树之中。
E element = getFloorTree(root.right, item);
return null == element ? root.item : element;
}
}当前子树中向上取整
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18private E getCeilingTree(Node<E> root, E item) {
// 当前子树为空,直接返回空节点即可。
if (null == root) {
return null;
}
if (comparator.compare(root.item, item) > 0) {
// 当前子树根节点值大于给定元素,ceiling(item)可能就是当前元素,或者位于左子树之中。
E element = getCeilingTree(root.left, item);
return null == element ? root.item : element;
} else if (comparator.compare(root.item, item) == 0) {
// 当前子树根节点值等于给定元素,直接返回即可。
return root.item;
} else {
// 当前子树根节点值小于给定元素,ceiling(item)一定位于右子树之中。
return getCeilingTree(root.right, item);
}
}当前子树中查找第 $k$ 个元素 (k从0开始)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18private E selectTree(Node<E> root, int k) {
// 当前子树为空,直接返回空节点即可。
if (null == root) {
return null;
}
int leftNum = size(root.left);
if (leftNum > k) {
// 左子树元素个数大于k,则直接到左子树中查找即可。
return selectTree(root.left, k);
} else if (leftNum == k) {
// 第leftNum个元素就是当前子树根节点
return root.item;
} else {
// 左子树元素个数小于k,则应当到右子树中找寻第(k - leftNum - 1)个元素。
return selectTree(root.right, k - leftNum - 1);
}
}当前子树中查看指定元素排名
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18private int rankTree(Node<E> root, E item) {
// 根节点为空,表明找不到元素,应当返回一个无穷负数
if (null == root) {
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
int leftNum = size(root.left);
if (comparator.compare(root.item, item) > 0) {
// 当前子树根节点值大于指定元素,则表明指定元素应当位于左子树之中。
return rankTree(root.left, item);
} else if (comparator.compare(root.item, item) == 0) {
// 二者相等,表明找寻的就是该节点。而该节点排名就是leftNum。
return leftNum;
} else {
// 当前子树根节点值小于指定元素,应该在右子树中查找该元素。并且该元素排名应当为右子树中排名 + leftNum + 1。
return leftNum + 1 + rankTree(root.right, item);
}
}当前子树中删除最小元素,并返回删除最小元素后的该子树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17private Node<E> deleteMinTree(Node<E> root) {
// 当前子树为空,直接返回空节点即可。
if (null == root) {
return null;
}
if (null == root.left) {
// 当前子树根节点的左儿子为空,表明这是最左节点。删除该节点后,直接以右子树作为当前子树即可。
root = root.right;
} else {
// 当前子树根节点的左儿子不为空,则在左子树中删除最小值。
root.left = deleteMinTree(root.left);
}
reSize(root);
return root;
}当前子树中删除最大元素,并返回删除最大元素后的该子树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16private Node<E> deleteMaxTree(Node<E> root) {
// 当前子树为空,直接返回空节点即可。
if (null == root) {
return null;
}
if (null == root.right) {
// 当前子树根节点的右儿子为空,表明这是最右节点。删除该节点后,直接以左子树作为当前子树即可。
root = root.left;
} else {
// 当前子树根节点的右儿子不为空,则在右子树中删除最大值。
root.right = deleteMaxTree(root.right);
}
reSize(root);
return root;
}当前子树中删除指定元素,并返回删除指定元素后的该子树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29private Node<E> deleteTree(Node<E> root, E item) {
// 当前子树为空,直接返回空即可。
if (null == root) {
return null;
}
if (comparator.compare(root.item, item) > 0) {
// 当前子树根节点值大于给定元素,则待删除元素一定位于左子树。
root.left = deleteTree(root.left, item);
} else if (comparator.compare(root.item, item) < 0) {
// 当前子树根节点值小于给定元素,则待删除元素一定位于右子树。
root.right = deleteTree(root.right, item);
} else {
// 二者相等,表明当前子树根节点就是待删除节点。
// 如果左右儿子有一者为空,则直接以另一者表示的子树作为当前子树即可。
if (null == root.right) {
root = root.left;
} else if (null == root.left) {
root = root.right;
} else {
// 左右儿子均不为空。为保证删除节点后仍保持有序,将右子树中最小元素赋值给当前子树根节点,然后删除右子树中最小元素即可。
root.item = getMinTree(root.right);
root.right = deleteMinTree(root.right);
}
}
reSize(root);
return root;
}初始化
1 | public BinarySearchTree(Comparator<? super E> comparator) { |
查询
查询指定元素是否存在
1
2
3public boolean contains(E item) {
return containsTree(this.root, item);
}查询最小元素
1
2
3public E getMin() {
return getMinTree(this.root);
}查询最大元素
1
2
3public E getMax() {
return getMaxTree(this.root);
}向下取整(查找所有小于等于item中的最大元素)
1
2
3public E getFloor(E item) {
return getFloorTree(this.root, item);
}向上取整(查找所有大于等于item中的最小元素)
1
2
3public E getCeiling(E item) {
return getCeilingTree(this.root, item);
}查询第 $k$ 个元素
1
2
3public E select(int k) {
return selectTree(this.root, k);
}查看指定元素是第几个元素(即指定元素排名)
1
2
3public int rank(E item) {
return rankTree(this.root, item);
}操纵
树中添加元素
1
2
3public void add(E item) {
this.root = addTree(this.root, item);
}树中删除最小元素
1
2
3public void deleteMin() {
this.root = deleteMinTree(this.root);
}树中删除最大元素
1
2
3public void deleteMax() {
this.root = deleteMaxTree(this.root);
}树中删除指定元素
1
2
3public void delete(E item) {
deleteTree(this.root, item);
}
相关文章