数据结构-队列/栈
概述
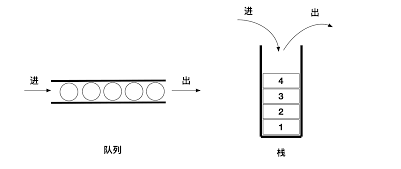
队列 属于一种特殊的线性表/链表,它仅允许从一端插入元素、另一端删除元素。
栈 属于一种特殊的线性表/链表,它仅允许在某一端插入、删除元素。
其结构图大致如下:
我们并不单独实现队列/栈,而是仅实现一个双端队列,它不仅具有队列功能、也具有栈功能。
双端队列实现方法有两种,一种基于循环数组,另一种基于链表。基于链表的已在 数据结构-链表 中给出,故而此处的双端队列基于循环数组实现。
结构
在 Java 库中,ArrayDeque 类为双端队列的实现。在这种实现方法中,其中无法存储 null 值。
我们采用 Java库中类似方法,并在稍后代码中给出无法存储 null 值的原因。
1 | class ArrayDeque<E> { |
实现
辅助方法
单增($0 \leq i < modulus$)
1
2
3
4
5
6private int inc(int i, int modulus) {
if ((++i) >= modulus) {
i = 0;
}
return i;
}多增
1
2
3
4
5
6private int inc(int i, int distance, int modulus) {
if((i += distance) >= modulus) {
i -= modulus;
}
return i;
}单减($0 \leq i < modulus$)
1
2
3
4
5
6private int dec(int i, int modulus) {
if ((--i) < 0) {
i = modulus - 1;
}
return i;
}多减
1
2
3
4
5
6private int sub(int i, int j, int modulus) {
if ((i -= j) < 0) {
i += modulus;
}
return i;
}扩容
第 9 行代码可以看到,它借用
null判断该双端队列为满状态还是空状态。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17private void grow() {
int oldCapacity = this.elementData.length;
Object[] elementData = new Object[oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1)];
// 将全部元素赋值过去
for (int i = 0; i < oldCapacity; i++) {
elementData[i] = this.elementData[i];
}
// 将原数组中右半部分元素移动到新数组中右半部分。
if (this.tail < this.head || (this.tail == this.head && null !=this.elementData[this.head])) {
int spaceCapacity = oldCapacity >> 1;
for (int i = this.head; i < oldCapacity; i++) {
elementData[i + spaceCapacity] = this.elementData[i];
}
this.head += spaceCapacity;
}
this.elementData = elementData;
}单增、多增、单减、多减四个函数意在封装下标移动时的取模操作。
初始化
空初始化
1
2
3public ArrayDeque() {
this(ArrayDeque.DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}带参数初始化
1
2
3
4
5public ArrayDeque(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
initialCapacity = 0;
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity + 1];
}查询
查询元素个数
我们无需变量存放元素个数信息,只需通过队首、队尾相减即可得到该信息。
1
2
3public int size() {
return sub(this.tail, this.head, this.elementData.length);
}查询双端队列是否为空
1
2
3public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}查询队首
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8// ArrayDequeu中二者是有差别的。如果双端队列为空,前者返回一个异常,后者返回null。对此我做了简化。
public E getFirst() {
return (E) this.elementData[this.head];
}
public E peekFirst() {
return getFirst();
}查询队尾
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8// ArrayDequeu中二者是有差别的。如果双端队列为空,前者返回一个异常,后者返回null。对此我做了简化。
public E getLast() {
return (E) this.elementData[dec(this.tail, this.elementData.length)];
}
public E peekLast() {
return getLast();
}操纵
队首添加元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15// ArrayDequeu中二者是有差别的。如果双端队列为空,前者返回一个异常,后者返回null。对此我做了简化。
public void addFirst(E e) {
if (null == e) {
return;
}
this.elementData[this.head = dec(this.head,this.elementData.length)] = e;
if (this.head == this.tail) {
grow();
}
}
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}队尾添加元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16// ArrayDequeu中二者是有差别的。如果双端队列为空,前者返回一个异常,后者返回null。对此我做了简化。
public void addLast(E e) {
if (null == e) {
return ;
}
this.elementData[this.tail] = e;
this.tail = inc(this.tail,this.elementData.length);
if (this.head == this.tail) {
grow();
}
}
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}队首删除元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13// ArrayDequeu中二者是有差别的。如果双端队列为空,前者返回一个异常,后者返回null。对此我做了简化。
public E removeFirst() {
final E e = (E) this.elementData[this.head];
if (null != e) {
this.elementData[this.head] = null;
this.head = inc(this.head, this.elementData.length);
}
return e;
}
public E pollFirst() {
return removeFirst();
}队尾删除元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14// ArrayDequeu中二者是有差别的。如果双端队列为空,前者返回一个异常,后者返回null。对此我做了简化。
public E removeLast() {
final int index = dec(this.tail, this.elementData.length);
final E e = (E) this.elementData[index];
if (null != e) {
this.elementData[index] = null;
this.tail = index;
}
return e;
}
public E pollLast() {
return removeLast();
}清空双端队列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7public void clear() {
for (int i = this.head; i != this.tail; i = inc(i, this.elementData.length)) {
this.elementData[i] = null;
}
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
}
扩展
对队列/栈中元素施加以单调性质便形成了一种新的数据结构——单调队列/单调栈。在单调队列/单调栈中,所有元素按序单调递增或单调递增。
该种数据结构用途不太广泛,仅能处理一种特定问题—— Next Greater Element。例如:给你一个数组,返回一个等长的数组,对应索引存储着下一个更大元素,如果没有更大的元素,就存 -1。如果输入为 [2,1,2,4,3] ,输出应当为 [4,2,4,-1,-1] 。基于单调栈,从后往前存储数组元素即可解决此问题。