数据结构-线性表
概述
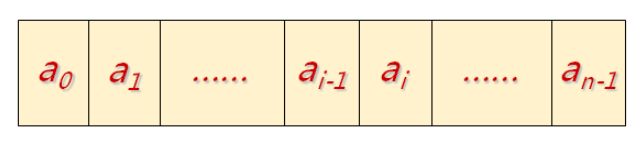
线性表 是具有线性结构特点、最简单、且最常用的一种数据结构。它是具有相同特性的数据元素组成的一个有限序列。
其结构图大致如下:
线性表的优缺点:
- 优点
- 随机存取。
- 无需额外空间保存元素间逻辑关系。
- 缺点
- 插入、删除需要移动大量元素。
- 可能存在存储空间“碎片“,即申请了但未使用的空间。
结构
线性表需要先申请一定空间,然后再想其中存放元素,因此存在 容量 和 元素个数 两个概念。其中 容量 指的是当前线性表可容纳的元素个数;元素个数 指的是当前线性表已容纳的元素个数。由于 Java 数组本身就保存容量信息,因此在此无需存储它,仅需存储元素个数即可。
1 | class ArrayList<E> { |
实现
辅助方法
扩容
每扩充一次,线性表容量增加一半。
1
2
3
4
5
6private Object[] grow() {
Object[] newElementData = new Object[this.elementData.length + (this.elementData.length >> 1)];
for (int i = 0;i < this.size; i++)
newElementData[i] = this.elementData[i];
return newElementData;
}初始化
空初始化
1
2
3public ArrayList() {
this(ArrayList.DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}带参数初始化
1
2
3
4
5public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
initialCapacity = 0;
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}查询
查询元素个数
1
2
3public int size() {
return this.size;
}查询线性表是否为空
1
2
3public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}查询元素位置
如果存在则返回其下标,否则返回 -1。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (null == o) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
if (null == this.elementData[i])
return i;
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
if (o.equals(this.elementData[i]))
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}查询指定位置内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7public E get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
return null;
} else {
return (E)this.elementData[index];
}
}操纵
指定位置添加元素
添加元素之前需要判断容量是否足够,不够则扩容。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14public boolean add(int index, E element) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size) {
return false;
} else {
if (this.elementData.length == this.size) {
this.elementData = grow();
}
for (int i = this.size; i >= index; i--)
this.elementData[i + 1] = this.elementData[i];
this.elementData[index] = element;
this.size = this.size + 1;
return true;
}
}线性表末添加元素
1
2
3public boolean add(E element) {
return add(size(),element);
}删除指定位置元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13public E remove(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
return null;
} else {
E oldElement = (E) this.elementData[index];
for (int i = index; i < this.size; i++) {
this.elementData[i + 1] = this.elementData[i];
}
this.size = this.size - 1;
this.elementData[this.size] = null;
return oldElement;
}
}清空线性表
1
2
3
4
5public void clear() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++)
this.elementData[i] = null;
this.size = 0;
}修改指定位置元素
修改指定位置元素并返回旧元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public E set(int index, E element) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
return null;
} else {
E oldElement = (E)this.elementData[index];
this.elementData[index] = element;
return oldElement;
}
}
扩展
将 “分块思想” 应用于线性表之中,便得到了一种新的数据结构——块状数组。块状数组将首先对整个数组进行分块处理,所有针对数组的操作,将首先施加于分块之上,然后进一步施加于分块所在的块数组之上。
块状数组之上各种操作的时间复杂度均为 $O(\sqrt{N})$,其常用于区间求和、区间查询等问题。
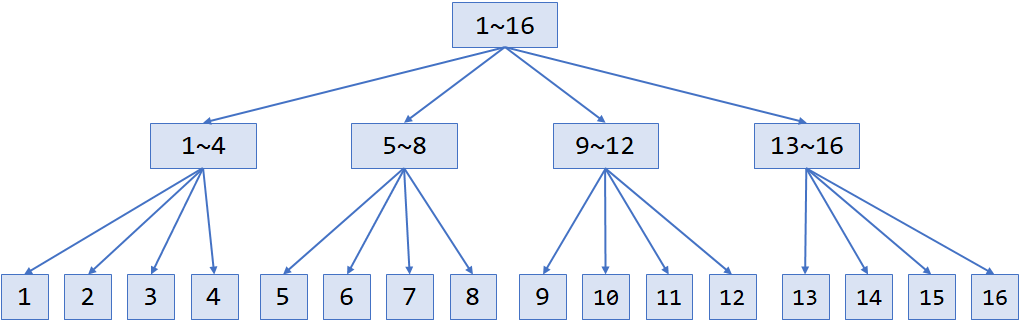
块状数组代码实现比较灵活,故而在此简单介绍思想即可。
相关文章